- Augusta University
- Centers & Institutes
- Vascular Biology Center
- Ruth Caldwell - Research & Publications
Ruth Caldwell - Research & Publications
← Back to main
Jump to: Research Interests Research Projects Spotlight Publications Recent Publications
Research Interests
Dr. Caldwell’s research, supported by grants from the NIH, VA and the AHA, seeks to elucidate the cellular and molecular mechanisms of retinal neurovascular injury and pathological angiogenesis in order to identify new therapies to limit damage and promote repair. Current studies seek to determine the specific role of the urea and ornithine generating metallo-enzyme arginase in retinal neurovascular injury and repair and to develop therapies targeting this enzyme and its downstream targets. Studies are also underway to develop new therapies targeting retinal cholesterol metabolism as a therapy for retinopathy of prematurity.
Research Projects
The arginase enzyme: Scheme for the catabolism of l-arginine to l -ornithine/urea or l-citrulline/NO, production of polyamines and anabolism and catabolism of proline. Also shown are the pathway for synthesis of l-arginine from l-glutamine, the reversible pathway between l-ornithine and l-glutamine, and the recycling of l-citrulline into l-arginine. ASL, argininosuccinate lyase; ASS, argininosuccinate synthase; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; OAT; ornithine aminotransferase; ODC, ornithine decarboxylase; OTC, ornithine transcarbamylase. Arginase (top left) is the final enzyme in the urea cycle within the liver, which restarts the cycle through the synthesis of l-citrulline from carbamoyl-phosphate (1) and l-ornithine (2) by OTC (middle). It should be noted that not all of these reactions occur within a given cell. In particular, the urea cycle is independent of the other reactions, i.e., l-arginine produced in the urea cycle is not a substrate for NOS and l-ornithine produced in the urea cycle is not a substrate for OAT or ODC.
We have various ongoing projects investigating the role of the arginase pathway in different retinal pathology models. The models we use in lab include mouse models of diabetic retinopathy (Akita mice and STZ models of type 1 diabetes, as well as the high fat diet induced obesity model of type 2 diabetes), traumatic optic neuropathy (TON), retinal ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury, and oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR) model. Our lab has extensive expertise in these disease models. We utilize different biochemical, molecular, and histological assays as well as different retinal functional and imaging analyses to examine retinal neurovascular injury.
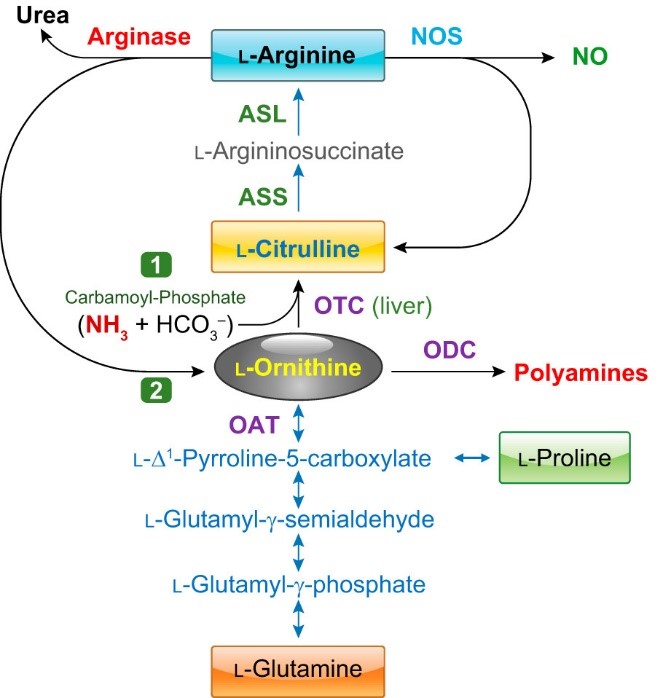
Figure & description are from our recent article in ‘Physiological Reviews’:
Arginase: A Multifaceted Enzyme Important in Health and Disease. R. William Caldwell, Paulo C. Rodriguez, Haroldo A. Toque, S. Priya Narayanan, and Ruth B. Caldwell. 07 FEB 2018https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00037.2016
