The Department of Neurology at the Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University aims for the highest quality of clinical care, the best training experience for our medical students, residents, and fellows, and the performance of cutting-edge research.
Our teaching mission includes medical students, residents, and fellows undergoing advanced training. Research activities in the department include both basic science and clinical and translational investigations. Additionally, our multidisciplinary Neuroscience Center of Excellence facilitates active collaborations with subspecialists from other departments including general neurosurgery, neuroradiology, neuro-otology, neuro-ophthalmology, functional neurosurgery (deep brain stimulation and epilepsy surgery), neuro-gastroenterology and basic science. Our facility houses a wide variety of other specialties including a level I trauma center, and seven ICUs (neurology, shock trauma, surgery, pediatric, neonatal, cardiology, and medical).
Neurological SubspecialtiesComprehensive CentersLinksNEUROLOGY News
Department of Neurology
Health Sciences Campus
706-721-4581
706-721-1459



Comprehensive Stroke Center
A pioneering 29 stoke/telestroke network and a JC certified Comprehensive Stroke Center
(first in Georgia)
National Parkinson’s Foundation Center of Excellence
NAEC Level 4 Epilepsy Center
An ALS Association Certified Treatment Center of Excellence
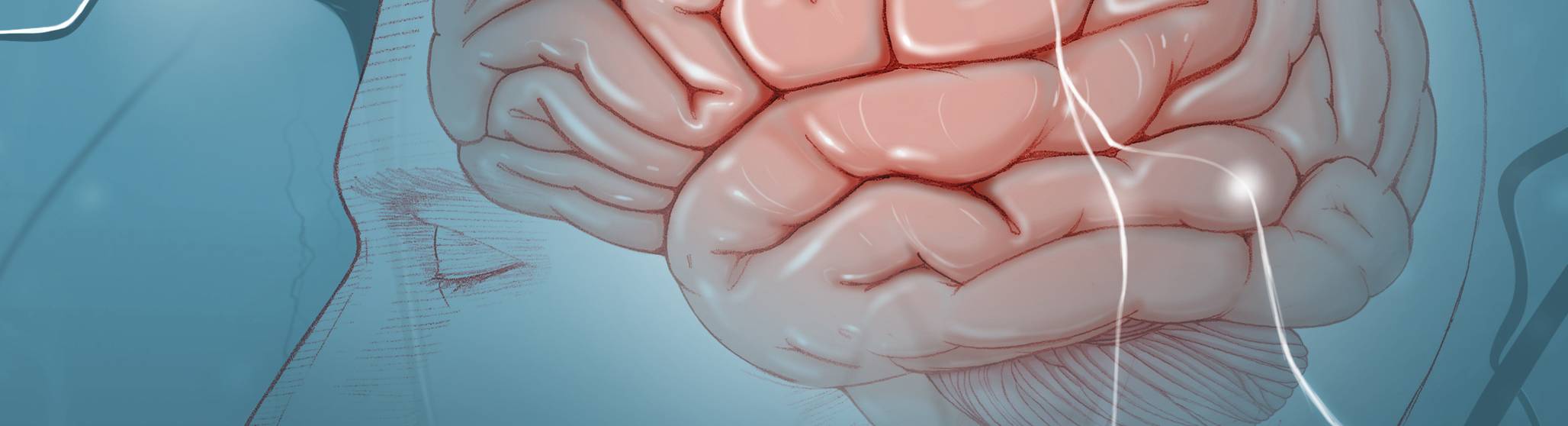
Neurology Alumni
The Neurology Network connects MCG Neurology Alumni together with their peers
Contact us at neurograndrounds@augusta.edu with questions about how to join.



